Tryptamine CAS 61-54-1
MOQ:1KG
Availability: On Order
Packaging: Regular packaging or customised
Please enquire for more information about Tryptamine including the price, delivery time and more detailed product information at WhatsApp
- Description
- Our Policy
Description
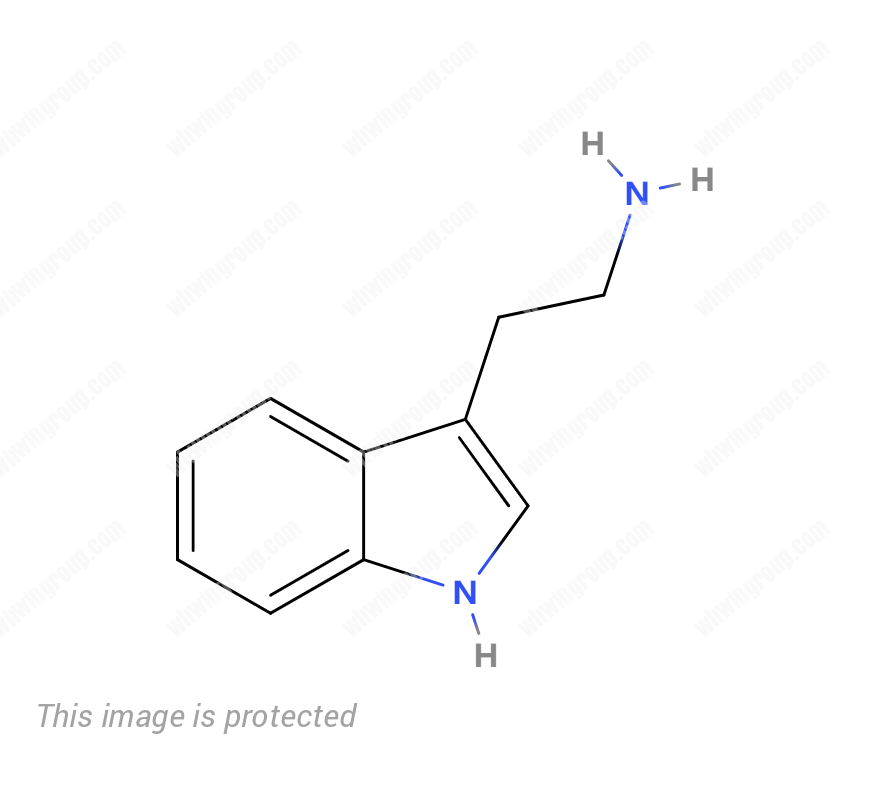
Tryptamine CAS 61-54-1 Product Information
| Product Name: | Tryptamine |
| Synonyms: | 2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)ethylamine;Tryptamine;1H-Indole-3-ethanamine;2-indol-3-yl-ethylamine;Indole-ethylamine;L-TRYPTAMINE;EINECS 200-510-5;2-Indol-3-yl-aethylamin;Tryptamin;3-Indoleethanamine;2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)ethanamine;MFCD00005661;TRYPTAMINE(P);125513;T56 BMJ D2Z;[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)-ethyl]amine;TRIPTAMINE;(1H-indol-3-yl)ethanamine;2-indol-3-ylethylamine |
| CAS NO: | 61-54-1 |
| Molecular Weight: | 160.22 |
| Molecular Formula: | C10H12N2 |
| Boiling Point: | 137 °C/0.15 mmHg (lit.) |
| Melting point: | 113-116 °C (lit.) |
| Density: | 0.9787 (rough estimate) |
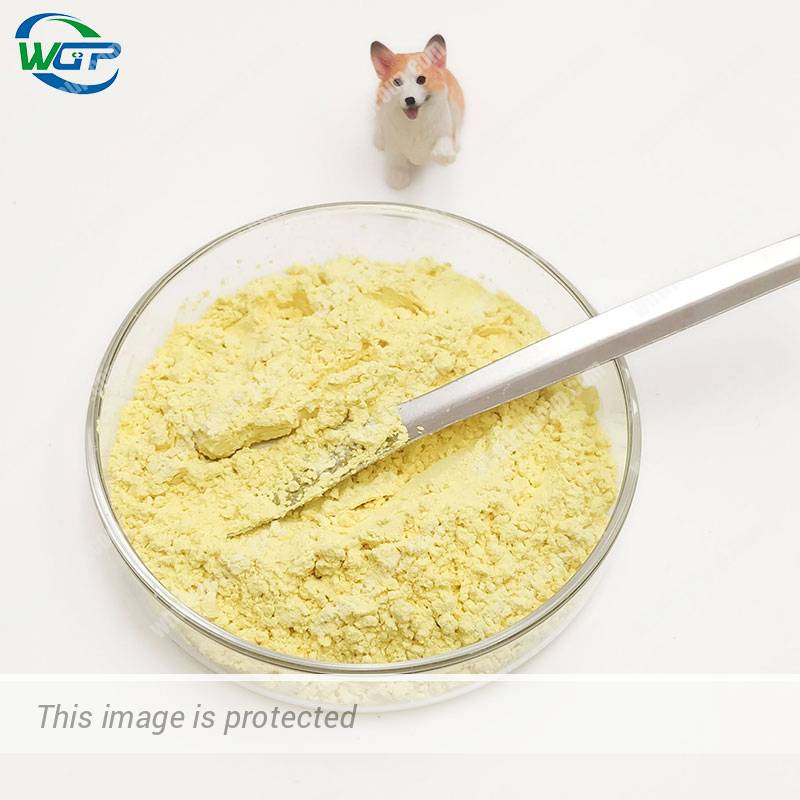
| Appearance: | White or pale yellow powder |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Solubility: | Store in a dry place at 4°C. |
| Storage: | slightly soluble in water |
What is tryptamine powder?
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid, similar to other trace amines, is believed to play a role as a neuromodulator or neurotransmitter.It is an aminoalkylindole consisting of indole having a 2-aminoethyl group at the 3-position. It has a role as a human metabolite, a plant metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is an aminoalkylindole, an indole alkaloid, an aralkylamino compound and a member of tryptamines. It is a conjugate base of a tryptaminium.
What is tryptamine used for?
Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems.In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility.Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a potential treatment target for neuropsychiatric disorders.
tryptamine synthesis
Tryptamine, a monoamine alkaloid containing an indole ring structure is derived by the decarboxylation of amino acid tryptophan.

The synthesis of tryptamines is typically conducted following a classic route starting with a Mannich reaction of an indole heterocycle, followed by quaternization of the amine, nucleophilic substitution with highly toxic cyanide and final reduction.
is lsd a tryptamine
LSD is not a tryptamine. It is a synthetic compound that belongs to the ergoline family of drugs.
tryptamine supplement
Tryptamine is a naturally occurring monoamine alkaloid. It is found in trace amounts in the brains of mammals and is hypothesized to play a role as a neuromodulator or neurotransmitter
| Transit time | You will normally receive your parcel within 7-15 working days after shipment (this may be delayed in special circumstances, such as Chinese New Year). |
| Receiving method | Generally we will send the goods by courier or special line, of course, if the goods themselves in the local warehouse have goods, also support self-pickup, depending on the circumstances. |
| Overseas warehouse | We have overseas warehouses in some European countries and Australia, such as Germany, Russia and Australia. |
| Delivery Method | WGP will ship via courier companies such as DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT or EMS. |
| About After Sales | Within 7 days of your receipt of the goods if you find any problems with the goods (broken packaging, less hair, etc.) please feel free to contact our sales, we will help you deal with it in time. |






-400x400.jpg)




1 review for Tryptamine CAS 61-54-1
Oren Benin
06/27/2022 at 5:10 AM
thank you lilly , very helpfull , always answear fast and ready to help