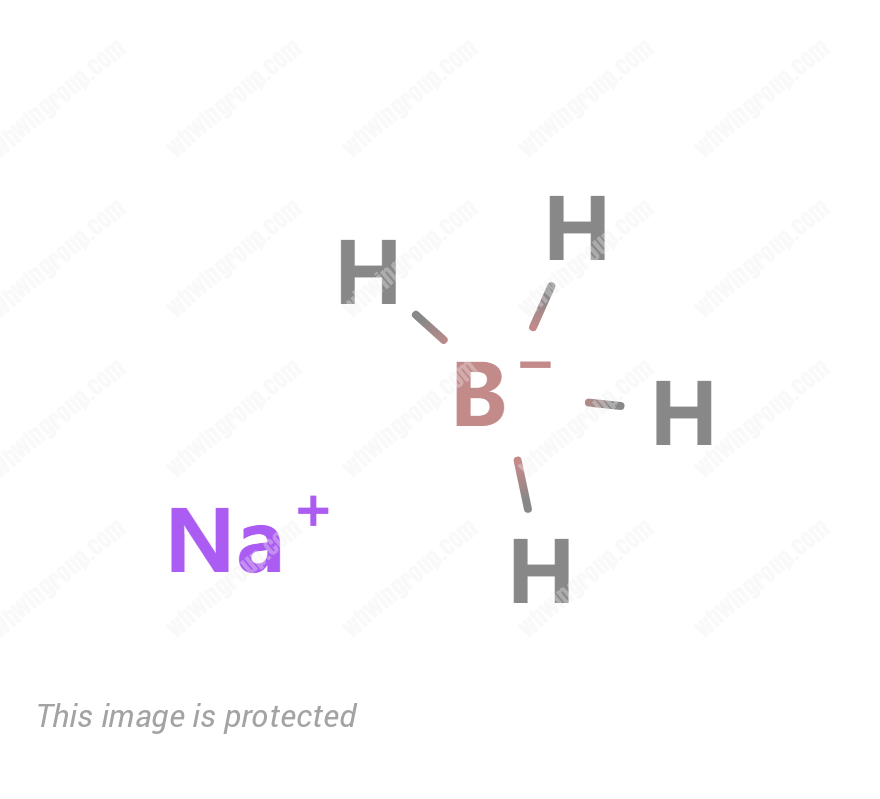
Sodium borohydride
CAS 16940-66-2
MOQ:1KG
Availability: On Order
Packaging: Regular packaging or customised
Please enquire for more information about Sodium borohydride including the price, delivery time and more detailed product information at WhatsApp
Description
Sodium Borohydride CAS 16940-66-2 Product Information
| Product Name: | Sodium borohydride |
| Synonyms: | VenPure SF;SodiuM borohydride caplets (18 x 10 x 8 MM), 98%;SodiuM borohydride granular, 10-40 Mesh, 98%;SodiuM borohydride granular, 99.99% trace Metals basis;SodiuM borohydride powder, >=98.0%;SodiuM borohydride puruM p.a., >=96% (gas-voluMetric);SodiuM borohydride ReagentPlus(R), 99%;SodiuM borohydride solution 2.0 M in triethylene glycol diMethyl ether |
| CAS NO: | 16940-66-2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 37.83 |
| Molecular Formula: | BH4Na |
| Boiling Point: | 500°C |
| Melting point: | >300 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Density: | 1.035 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Appearance: | White powder |
| Purity: | >98% |
| Stability: | Water Solubility 550 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Storage: | Store at RT. |
sodium borohydride reduction
Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a commonly used reducing agent in organic chemistry. It is widely employed for the reduction of various functional groups, including aldehydes, ketones, and certain imines. The reduction with sodium borohydride typically proceeds as follows:
1. Hydride Transfer:
Sodium borohydride acts as a source of hydride ions (H-) in the reaction. The hydride ion is transferred from the NaBH4 reagent to the electrophilic carbon atom of the targeted functional group.
2. Addition to Carbonyl Group:
In the case of carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones), the hydride ion adds to the polarized carbon-oxygen double bond, resulting in the formation of an alkoxide intermediate.
3. Protonation:
The alkoxide intermediate is then protonated by a solvent or an acidic additive present in the reaction mixture. This step leads to the formation of the reduced alcohol product.
Overall, sodium borohydride reduction provides a relatively mild and selective means of reducing carbonyl groups to alcohols. However, it is worth noting that sodium borohydride is not effective for reducing certain functional groups, such as esters, amides, and carboxylic acids. In those cases, more powerful reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) may be required.
sodium borohydride reduction mechanism
sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a commonly used reducing agent for converting aldehydes and ketones to their corresponding alcohols. The reduction mechanism of sodium borohydride involves the direct reaction of the hydrogen atom of BH4- ion with the oxygen atom of the functional group, followed by the formation of an intermediate and further reaction to yield the reduced product
sodium borohydride reaction with water
sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is an inorganic compound that is soluble in protic solvents such as water and lower alcohols. When sodium borohydride is dissolved in water, it decomposes to produce sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The reaction can be represented as follows:
NaBH4 + 2H2O → NaOH + 4H2
The reaction is exothermic and hydrogen gas produced is highly flammable.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.